If you’ve been experiencing persistent shoulder pain and limited movement, you might be dealing with shoulder impingement. For many, the pain can become unbearable, making daily tasks like reaching, lifting, or even sleeping uncomfortable. One effective solution to this problem is Shoulder Tuberoplasty—a surgical procedure designed to alleviate the symptoms of impingement and restore normal function to the shoulder joint.
In this post, we’ll take a closer look at what shoulder tuberoplasty involves, who might benefit from it, and what you can expect during recovery.
What is Shoulder Tuberoplasty?
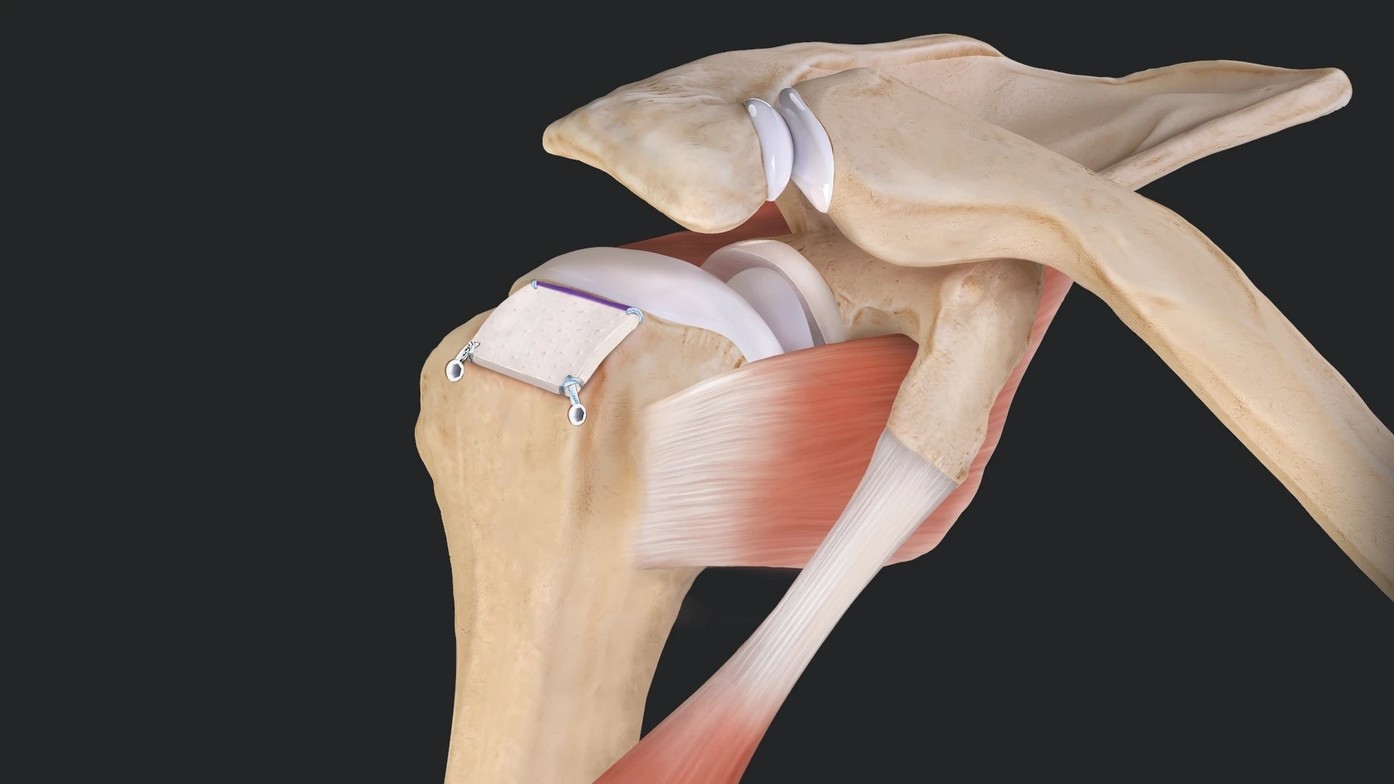
Shoulder tuberoplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at treating shoulder impingement syndrome. The surgery involves reshaping or smoothing the humeral tuberosity (the bony prominence at the top of the upper arm) to create more space within the shoulder joint. By increasing space, this procedure can reduce friction and prevent the rotator cuff from getting pinched or irritated, providing long-term relief.
How Shoulder Tuberoplasty Works
During the surgery, a surgeon makes small incisions and uses arthroscopic tools to remove bone spurs and reshape the bony area of the humerus. This relieves pressure on the rotator cuff tendons, which can become irritated and inflamed due to impingement.
Who is a Candidate for Shoulder Tuberoplasty?
Patients suffering from chronic shoulder pain caused by impingement syndrome that hasn’t responded to non-surgical treatments (such as physical therapy, injections, or medication) might be good candidates for shoulder tuberoplasty. This procedure is often recommended when there is evidence of bony growths (osteophytes) or deformities contributing to the impingement.
Symptoms of Shoulder Impingement
Before considering surgery, it’s essential to understand the symptoms of shoulder impingement. Some common signs include:
- Persistent Shoulder Pain: Pain during lifting, reaching, or overhead activities.
- Restricted Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the shoulder, especially when raising the arm.
- Weakness: Reduced strength in the shoulder, making simple tasks like lifting objects difficult.
- Pain During Rest: Sharp pain when lying on the affected shoulder or during rest.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, consulting with a specialist is crucial to determine the severity of the condition and discuss potential treatment options like tuberoplasty.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Shoulder Impingement
Before resorting to surgery, many patients try non-surgical treatments to alleviate their symptoms. Some of the most common include:
Physical Therapy
Targeted exercises can help strengthen the rotator cuff muscles and increase flexibility, which may reduce impingement. A trained physical therapist will work with you on specific movements to improve mobility and reduce discomfort.
Corticosteroid Injections
In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections might be recommended to reduce pain and swelling in the short term. However, injections aren’t a long-term solution.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Over-the-counter or prescription NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can reduce pain and inflammation associated with shoulder impingement.
The Shoulder Tuberoplasty Procedure
If non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, shoulder tuberoplasty may be the next step. Here’s what the procedure typically involves:
Step 1: Pre-Surgical Evaluation
Before surgery, your doctor will assess the severity of your impingement through imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. This evaluation helps determine the precise location of the impingement and any bony abnormalities that need correction.
Step 2: Arthroscopic Surgery
Shoulder tuberoplasty is minimally invasive, meaning it’s usually performed using an arthroscope. Small incisions are made around the shoulder, and a tiny camera is inserted to guide the surgeon as they remove bone spurs and reshape the humerus.
Step 3: Recovery and Rehabilitation
After surgery, the recovery process begins. Most patients will be given a rehabilitation plan, which includes:
- Rest and Immobilization: The shoulder is typically immobilized in a sling for a few weeks to allow healing.
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program will help you regain strength and mobility in the shoulder.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups with your surgeon will track progress and ensure a full recovery.
Benefits of Shoulder Tuberoplasty
The primary goal of shoulder tuberoplasty is to relieve pain and restore function to the shoulder joint. Here are the key benefits:
Pain Relief
By removing bone spurs and reducing impingement on the rotator cuff, tuberoplasty can significantly reduce or eliminate pain caused by shoulder impingement.
Improved Range of Motion
After surgery and rehabilitation, many patients experience a greater range of motion, allowing them to resume normal activities without pain or restriction.
Minimally Invasive Procedure
Since tuberoplasty is performed arthroscopically, it involves smaller incisions, less tissue damage, and a faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.
What to Expect During Recovery
Recovery from shoulder tuberoplasty varies depending on the severity of the impingement and the individual’s overall health. Most patients can expect the following stages during recovery:
First Few Weeks
During the first few weeks, you’ll need to keep your shoulder immobilized to protect the area and allow initial healing. You might experience some discomfort, which can be managed with prescribed pain medications.
Physical Therapy
Around 4-6 weeks after surgery, you’ll begin physical therapy. This is a critical part of the recovery process, as it helps restore strength and mobility to the shoulder. The goal is to gradually increase your range of motion without putting too much strain on the healing tissues.
Return to Normal Activity
Most patients can return to light activities within 3 months, but full recovery can take up to 6 months. It’s essential to follow your rehabilitation plan closely and avoid overexertion during this time.
Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, shoulder tuberoplasty carries some risks, including:
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Scar tissue formation
- Incomplete pain relief
However, the minimally invasive nature of the procedure helps reduce the risk of complications, and most patients recover without issues.
Conclusion: Is Shoulder Tuberoplasty Right for You?
If shoulder impingement is limiting your life and non-surgical treatments haven’t worked, shoulder tuberoplasty might be the solution you need. By consulting with a shoulder specialist, you can determine whether this minimally invasive procedure is right for you and take the next steps toward pain relief and restored mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does it take to recover from shoulder tuberoplasty?
Recovery typically takes 3-6 months, depending on the severity of the impingement and the individual’s health. Physical therapy is essential for a full recovery.
2. Is shoulder tuberoplasty a major surgery?
Shoulder tuberoplasty is considered a minimally invasive surgery because it’s performed arthroscopically. This usually results in smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
3. Will I need physical therapy after shoulder tuberoplasty?
Yes, physical therapy is a critical part of recovery. It helps restore strength and mobility to the shoulder after surgery, ensuring a successful outcome.
4. What are the risks of shoulder tuberoplasty?
Risks include infection, nerve damage, and scar tissue formation, though these are rare. Your surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the procedure.
5. Who is a good candidate for shoulder tuberoplasty?
Candidates are typically individuals with chronic shoulder impingement who haven’t responded to non-surgical treatments like physical therapy or injections.
Source: